

These two RSs, however, were developed by enrolling patients mostly from countries in North America, South America and Europe, with only Australia and New Zealand providing data from Asian countries to the GRACE registry. This scoreis derived from a more representative community-based registry. The second most commonly used score is the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk model, 5 which uses eight variables and is applicable to the entire spectrum of ACS. For non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), the TIMI score is based on seven clinical indicators with scores ranging from 0 to 7. For ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the TIMI score is based on eight clinical indicators available on admission with scores ranging from 0 to 14. The most widely used RS is the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) algorithm, 3, 4 which is simple to calculate and is derived from selected clinical-trial cohorts. Furthermore, stratification of the risk of ACS using tools such as risk scores (RSs) is recommended by practice guidelines. 1 Identifying high-risk patients, and hence selecting those who would benefit from more aggressive treatment, is essential for the management of ACS. Conclusions: TIMI risk score can be used for long term prognostication of NSTE-ACS patients after revascularization, and thus can be used by clinicians for therapeutic decision making.Despite advances in treatment, acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is still associated with significant mortality. The relative risk increased by 66% as the TIMI risk score increased from low risk category (TIMI score 0-2) to high risk (TIMI score 5-6). Event rates increased significantly as the TIMI risk score increased as determined by regression analysis (p=0.004). The event rates of the primary endpoint and its components after 36 months were 26.6%. Results: Baseline characteristics for 150 participants were as follows, age 56☙.5 years, 78.7% male, 25% diabetics, 82% hypertensives, and 36% had hypercholesterolemia. Clinical secondary endpoints included the individual components of the primary endpoint, death, nonfatal recurrent MI, and repeat target vessel revascularization. The primary endpoint was a composite of MACE ( death, repeat target-vessel revascularization, and non-fatal recurrent MI) at the end of 36 months of follow up. TIMI risk score was calculated for each patient at admission. Methods: This was a retrospective observational cohort study of consecutive NSTE-ACS patients (n=150) treated by percutaneous coronary intervention between January 2017 to June 2017 in a tertiary care center. This study aims at assessing the long term prognostic significance of TIMI risk score, 36 months after revascularization in NSTE-ACS.
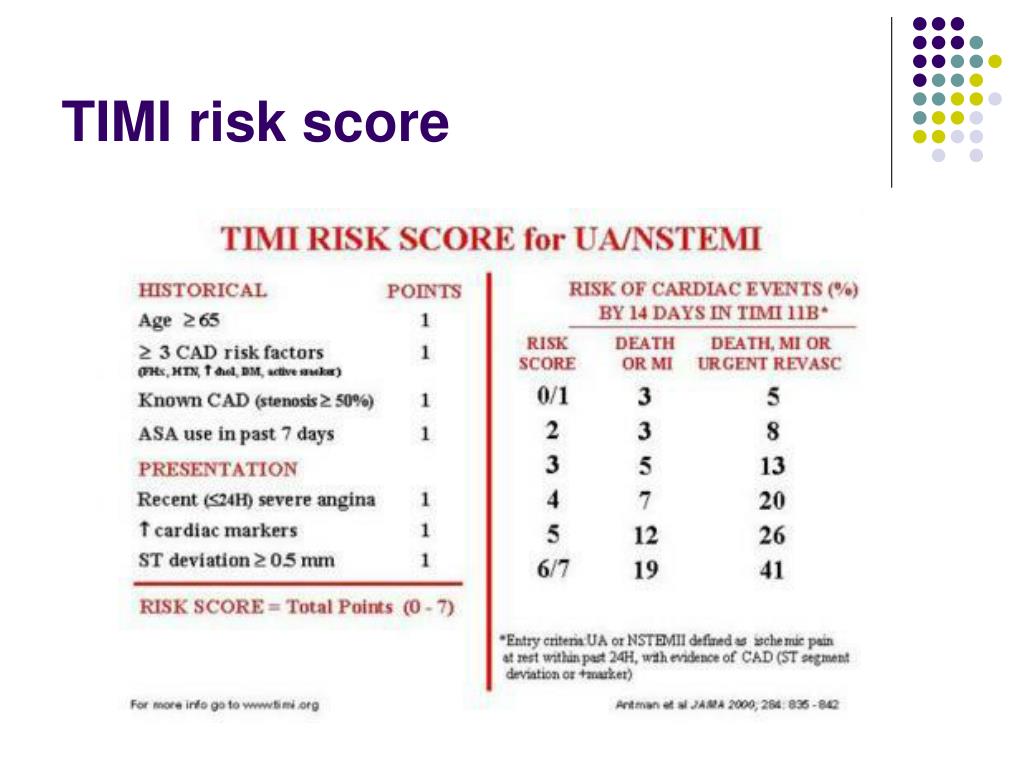
However, few studies have evaluated the long term prognostic significance of TIMI risk score after revascularization. Primarily thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) risk score was developed to guide therapy and assess the short term (14 days) prognosis of these patients.

ABSTRACT Background: Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) patients are complex and varied population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
